Course Design Tip: Test the Learner’s Assumptions
Author:
Go to Source

In a previous post, we looked at how context helps frame the learning experience. It keeps us from just doing an information dump as we add clarity about our learners and the learning objectives.
One way to establish context is by learning what the user already knows. Test their assumptions. This does two things:
- Expose their current level of understanding. This helps them see what they do or don’t know about the subject.
- Demonstrate what level of knowledge/competence is required to meet the learning objectives.
How to Test the Learner’s Assumptions
Generally, you can do one of two things to test the learner’s understanding and assumptions around a given subject.
Create a Pre-Assessment
The easiest thing is to create a pre-assessment. Usually, pre-assessments are used to filter the learner. Pass the assessment, go to the end. Fail the assessment, start the course.
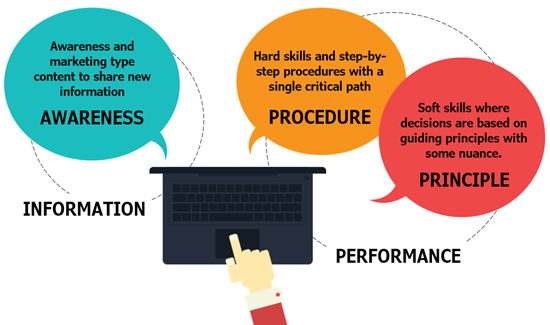
For procedural training, that is step-by-step, the filtering makes sense. You either know the procedures or not. For principle-based training, we want to expose the understanding (or assumptions for experienced people).
In this case, we use the pre-assessment to help them understand where they’re at. We’re not using it to filter them away from the course.
Create a Simple Scenario
I like to throw people in the pool and get them to make real world decisions as soon as possible. So, I recommend some sort of early decision-making interactions. They don’t need to be big elaborate scenarios: just a few interactions that test their understanding and help them see what they currently know about a given situation. And then from there, work through the content.
In most cases, the learners already have existing knowledge and probably a pretty good idea of what the course will teach. With that comes some bias and possibly incorrect understanding. By getting them to make decisions related to the content, you expose to them what they know or possibly don’t know.
The main point in all of this is to get them to think about what they know about the topic before going through the topic. People can easily figure out and compare what they thought versus what they’re presented. But your interaction gets them set up to do so.
In either case, get them to test what they know before giving them the content.
Download the fully revised, free 63-page ebook: The Insider’s Guide to Becoming a Rapid E-Learning Pro
Upcoming E-Learning Events
April 20 & 21(Brisbane). Postponed until September. Details coming soon. Articulate Roadshow: Learn more and register here.April 23 & 24(Melbourne). Postponed until September. Details coming soon. Articulate Roadshow: Learn more and register here.- November 9 &10 (London). Details coming soon.
Free E-Learning Resources
 |
 |
 |
|
Want to learn more? Check out these articles and free resources in the community. |
Here’s a great job board for elearning, instructional design, and training jobs |
Participate in the weekly elearning challenges to sharpen your skills |
 |
 |
 |
|
Get your free PowerPoint templates and free graphics & stock images. |
Lots of cool elearning examples to check out |
Getting Started? This elearning 101 series and the free e-books will help. |
