S.1 Physics Lesson: Exploring the Kinetic Theory of Matter and States of Matter. 18TH MAY 2023
Video by Holistic Elearning Platform via YouTube
Source

In the fascinating world of physics, the study of matter and its different states plays a crucial role. In this S.1 Physics lesson, we will dive into the concepts of the Kinetic Theory of Matter and explore the various states of matter. By the end of this lesson, you will have a solid understanding of how particles behave in different states and the key characteristics of each state of matter.
1. The Kinetic Theory of Matter:
The Kinetic Theory of Matter is a fundamental concept that explains the behavior and properties of matter at the particle level. According to this theory, matter is composed of tiny particles in constant motion. These particles possess kinetic energy, and their behavior influences the macroscopic properties of matter.
2. Four States of Matter:
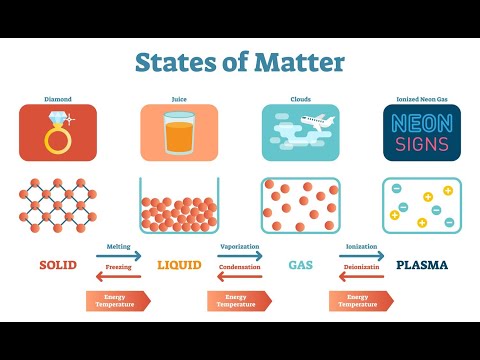
In our everyday experiences, matter exists in three primary states: solid, liquid, plasma and gas. Let’s delve into each state and understand their distinctive characteristics.
a. Solid: In the solid state, particles are closely packed and have strong forces of attraction between them. They vibrate in fixed positions and have a definite shape and volume.
b. Liquid: In the liquid state, particles are still close together but have weaker forces of attraction. They are free to move and slide past each other, allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of their containers. However, they have a definite volume.
c. Gas: In the gas state, particles are widely separated and have minimal forces of attraction. They move freely and randomly, filling the entire space available to them. Gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
d. Plasma: The plasma state is the fourth state of matter, characterized by highly energized particles that have lost their electrons. Plasma is often found in high-temperature environments or when gases are exposed to intense energy sources. It is composed of charged particles and exhibits unique properties such as the ability to conduct electricity. Examples of plasma include lightning and the sun.
3. Changes of State:
Matter can transition from one state to another through processes such as melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, and sublimation. These changes occur due to the gain or loss of thermal energy, affecting the particle motion and arrangement.
a. Melting and Freezing: Melting is the process of changing from a solid to a liquid state, while freezing is the reverse process from liquid to solid.
b. Evaporation and Condensation: Evaporation occurs when a liquid changes into a gas, while condensation is the reverse process from gas to liquid.
c. Sublimation: Sublimation is the process in which a solid directly converts to a gas without passing through the liquid state.
4. Examples and Applications:
We will explore real-life examples and applications of the states of matter, such as the water cycle, phase changes of substances, and the behavior of gases. These examples will help reinforce your understanding and illustrate the practical significance of the Kinetic Theory of Matter.
Conclusion:
The Kinetic Theory of Matter and the states of matter are fundamental concepts in physics that provide insights into the behavior of particles and the macroscopic properties of substances. Through this lesson, we have examined the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases, as well as the changes of state that matter can undergo. Understanding these concepts lays the foundation for further exploration in physics and other scientific disciplines.
