Transmission of impulses | Biology | Class 10 | Kerala Syllabus | CBSE
Video by BrainsPrep : Kerala Syllabus Learning App via YouTube
Source

Transmission of impulses | Biology | Class 10 | Kerala Syllabus | CBSE
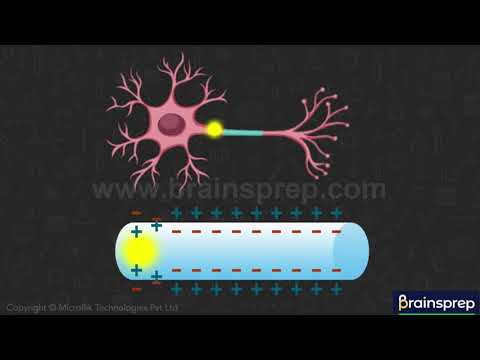
Now, let us see how the impulses are getting transmitter from one neuron to another, or simply throughout a neuron. How an impulse is moving impulses are simply messages that moves or is transmitted across the axon by all in the form of electric charge. Let us have a look at this in this figure, we are viewing a cylindrical body.
What is it? It is nothing but an enlarged view of the axon here can currently see a plus plus plus charges and a minus charge embedded. Which means positive charges are Amber that in the outside region of the plasma membrane, while the inside region of the plasma membrane is embedded with negative charge when no impulse is formed or when no signal or when no stimuli is given a cell or a neuron is set to be in the state of rec.
And this position, what happens is the outside of the plasma membrane remains for steel. Whereas the inside of the plasma membrane remains negative. When a stimulus is applied, what happens? Let’s see. When we apply a stimulus, it is for a very short period of time. And in a very short region present in the attic.
Here we are depicting that in as a shaded portion, as you can see in the figure, what happens in that chair, that portion is the polarity or the ionic equilibrium. Simply, it means that the positive charge outside the plasma membrane now migrates or comes inside. Whereas the negative charge present inside the plasma membrane goes outside.
This is the state that is occurring, which is called the. No worse. Remember one thing that this change in polarity or this change in ionic equilibrium is temporary. It lasts only for a few seconds. And after this few seconds, it reverts back to the normal. As in the case of rust that is posted outside the plasma membrane and negative charge inside the plasma.
Simultaneously when the chart in this shaded region rewards back to normal. Now the Addison area in the axon also rewards us. It’s polarity as shown in the figure. Now, likewise, this polarity change goes on propagating in a unidirectional fashion until it returns us the synaptic. Now. In this way, an impulse is transmitter through an act Sonic length.
